How The Digital Camera Works
How the digital camera works
How The Digital Camera Works:
| Sectional view of a camera |
Introduction:
A camera is an optical instrument for recording or capturing images, which may be stored locally, transmitted to another location, or both. The images may be individual still photographs or sequences of images constituting videos or movies. The camera is a remote sensing device as it senses subjects without physical contact. The word camera comes from camera obscure, which means "dark chamber" and is the Latin name of the original device for projecting an image of external reality onto a flat surface. The modern photographic camera evolved from the camera obscure. The functioning of the camera is very similar to the functioning of the human eye. The first permanent photograph of a camera image was made in 1826 by Joseph Nicéphore Niépce.
Parts of a Camera:
- Lens
- Viewfinder
- Body
- Shutter Release
- Aperture
- Image Sensor
- Memory Card
- LCD Screen
- Flash
| Parts of a camera |
Working:
The light enters the camera through the lens. Then the light rays gets refracted through the number of camera lens with different diffraction property. Then after the refraction the light rays reach a reflecting mirror which is placed at an angle of 45 degree. Then after reflection the light rays is deflected to 90 degree upwards and then the light rays reach the pentagon prism and it is refracted at the bottom on the pentagon prism and then the inner surface of the prism reflects the light rays 2 times and then the light rays get refracted and it could be seen in the eye piece
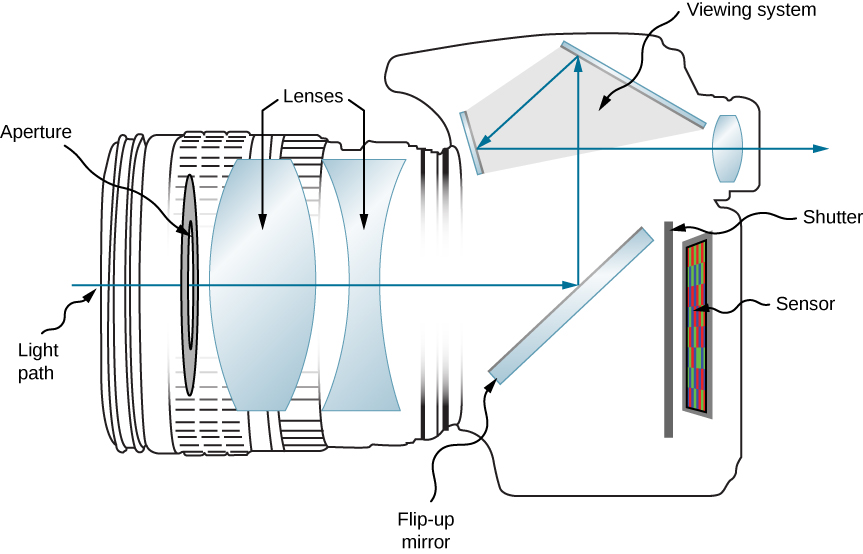 |
| Light path of a camera |
CMOS Sensor:
A CMOS sensor is an image sensor that contains most of its functioning parts on a single circuit.
It adds image sensing capabilities to devices, such as cell phone cameras and scanners, and
allows the user to convert a real life scene into a digital image.
A typical CMOS is an integrated circuit with an array of pixel sensors. Each pixel sensor
contains its own light sensor and active amplifier. An analog-to-digital converter and other
components critical to the operation of the pixel sensors are located on the CMOS sensor.
Light comes through the lens and is processed by the color filter before reaching the pixel sensor
array. When the filtered light reaches the pixel array, each pixel sensor converts the light into an
amplified voltage signal that can be further processed by the rest of the CMOS sensor.
Quach - 4
The CMOS sensor contains four main parts: the color filters, the pixel array, the digital controller,
and the analog to digital converter.
 |
| Parts of a CMOS Sensor |
Lens:
A camera lens (also known as photographic lens or photographic objective) is an optical lens or assembly of lenses used in conjunction with a camera body and mechanism to make images of objects either on photographic film or on other media capable of storing an image chemically or electronically.
There is no major difference in principle between a lens used for a still camera, a video camera, a telescope, a microscope, or other apparatus, but the detailed design and construction are different. A lens might be permanently fixed to a camera, or it might be interchangeable with lenses of different focal lengths, apertures, and other properties.
While in principle a simple convex lens will suffice, in practice a compound lens made up of a number of optical lens elements is required to correct (as much as possible) the many optical aberrations that arise. Some aberrations will be present in any lens system. It is the job of the lens designer to balance these and produce a design that is suitable for photographic use and possibly mass production.
 |
| Types of camera lens |
How to calculate the megapixel of the image:
The ratio of the cmos sensor should be determined it is mostly 3:2. By knowing the ratio of sensor and the resolution of the image shooed the megapixel of the camera could be determined.
So if your photo has this resolution:
3264 x 2448
Do the following simple calculation:
3264 x 2448 = 7,990,272
3264 x 2448 = 7,990,272
7,990,272 / 1,000,000 = 7.990272
So this image would basically be 8 Megapixels or 8MP. As a general rule you just round up or down accordingly.
1024 x 768 = 786432
0.7 Megapixel
0.7 Megapixel
1600 x 1200 = 1920000
2 Megapixel
2 Megapixel
2048 x 1536 = 3145728
3 Megapixel
3 Megapixel
3264 x 2448 = 7990272
8 Megapixel
8 Megapixel
This is how the camera works...
Thanks for reading hope you learned some thing new. To learn some thing new daily like the post and follow my blog.

Comments
Post a Comment